Differences between HPMC and MHEC in dry-mix applications
1. Chemical structure differences
HPMC:Contains hydroxypropyl (-O-CH2-CHOH-CH3) and methyl (-O-CH3) substituents.
MHEC: Contains methyl (-O-CH3) and hydroxyethyl (-O-CH2-CH2-OH) substituents.
Impact: Hydroxypropyl is slightly more hydrophobic than hydroxyethyl, resulting in different solubility and temperature response.
2. Solubility and gelation temperature
HPMC:Cold water dissolves more slowly and may take longer to disperse (especially in low viscosity products).
Thermal gelation temperature is higher (usually 60-90℃), more stable at high temperatures, suitable for hot environments.
MHEC:Faster dissolution and better dispersibility.
Thermal gelation temperature is lower (about 40-60℃), easy to gel at high temperatures, which may limit its use in hot climates.
3. Water retention capacity
HPMC: Stronger water retention, longer mortar open time, reduced water evaporation, suitable for dry environment or thick layer construction.
MHEC: Slightly weaker water retention, but may be more suitable for occasions that require moderate water release (such as rapid hardening requirements).
4. Viscosity and rheology
HPMC: Wide viscosity range (low to ultra-high viscosity), strong adjustability, providing better anti-sagging (suitable for vertical surface construction).
MHEC: Smoother rheology, better construction feel, may improve leveling efficiency.
5. Temperature stability
HPMC: Stable performance at high temperature (high gel temperature), suitable for hot areas or summer construction.
MHEC: Better performance in low temperature environment, high temperature easy gel may affect construction.
6. Compatibility with cement
HPMC: Excellent stability in a strong alkaline environment, good compatibility with most cements.
MHEC: May have better synergistic effects with certain additives (such as latex powder), but specific formula verification is required.
7. Cost and market application
HPMC: It is widely used and cost-effective, and is the mainstream choice for dry-mixed mortar.
MHEC: The price is usually higher, but it may perform better in certain areas (such as self-leveling mortar).
8. Typical application scenarios
HPMC:
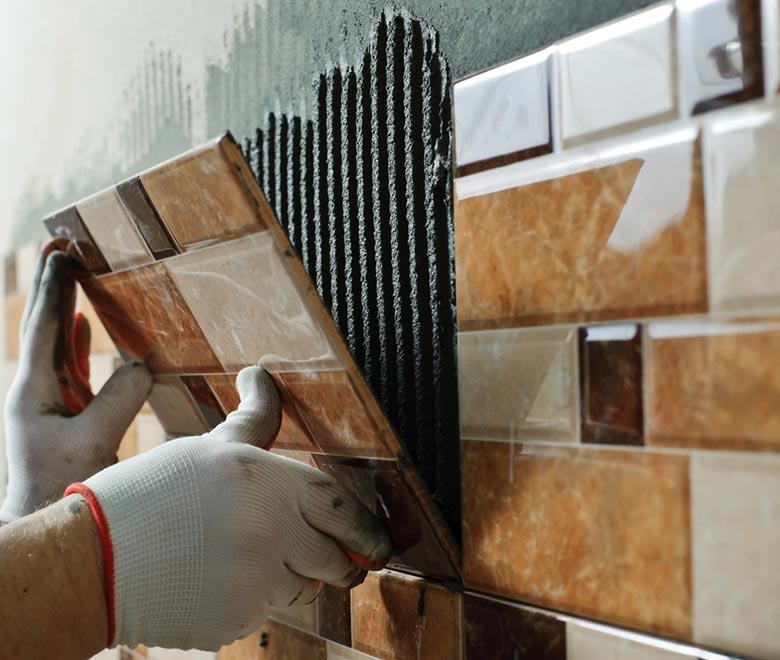
Exterior wall plastering, tile adhesive (requires high water retention and anti-sagging).
High temperature environment construction (such as floor mortar).
MHEC:
Self-leveling mortar (quick dissolution, good leveling).
Indoor putty (high construction smoothness requirements).
Name:Erica Wei
E-mail:erica@mailose.com