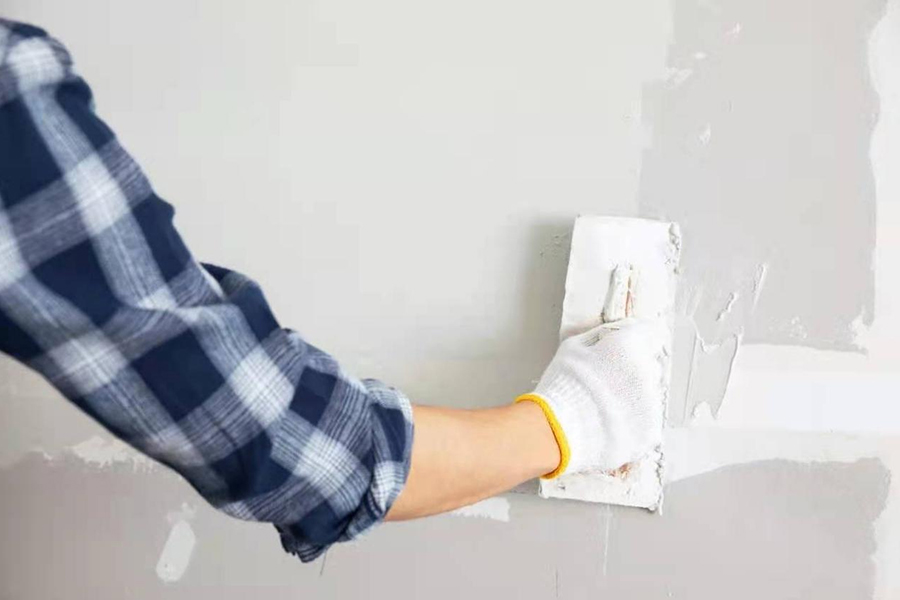
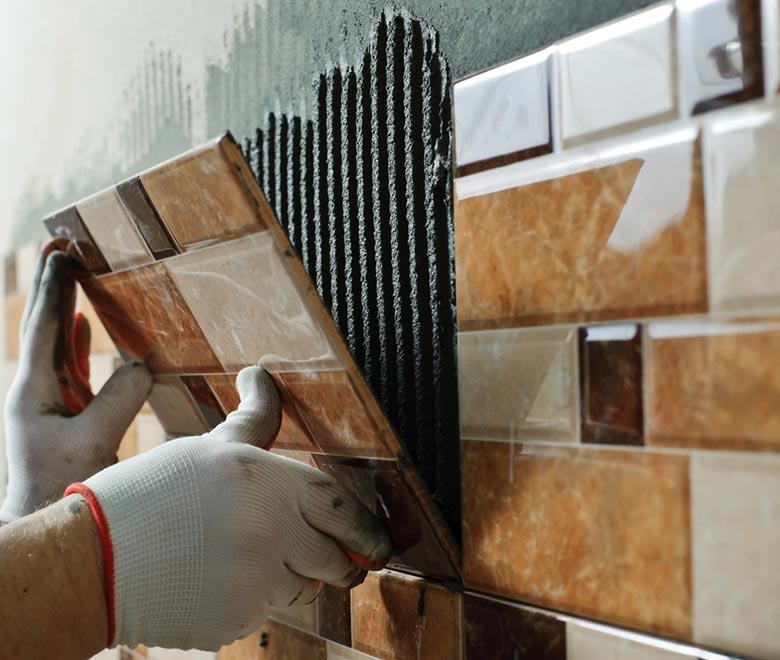
In the building and construction industry, the use of chemical additives has become an essential aspect of modern construction practices. One of the most widely used chemical additives in the industry is Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC). HPMC is a versatile material that can be used in various applications such as cement, plaster, and other construction materials. It is used to improve the performance of construction materials by enhancing properties such as workability, adhesion, water retention, and durability.
HPMC is a cellulose-based polymer that is derived from the natural plant material, cellulose. It is a non-ionic water-soluble polymer that can dissolve in cold water to form a clear, viscous solution. HPMC is widely used in the construction industry because of its unique properties such as high water retention, thermal gelation, and film-forming ability.

Mailose MP 200K(S)
Applications of HPMC in Construction
Adhesive
One of the most common uses of HPMC in the construction industry is as a adhesive in cement-based materials. HPMC acts as a dispersing agent, improving the workability of the cement and reducing the water content needed for a given mix. This, in turn, reduces the risk of cracking and shrinkage of the final product.
Thickener
In addition to being a dispersing agent, HPMC also acts as a thickener, providing the necessary viscosity to maintain the shape of the final product. This is particularly useful in applications such as rendering and plastering, where the material needs to maintain its shape on vertical surfaces without sagging or slumping.
Improve the Adhesion
Another important property of HPMC is its ability to improve the adhesion of the construction material to the substrate. HPMC can form a film on the surface of the substrate, which improves the bonding strength between the material and the substrate. This is particularly important in applications such as tiling, where the tiles need to be securely bonded to the substrate to prevent cracking and movement.
Water-Retention Agent
HPMC is also used in the construction industry as a water-retention agent. It can absorb and retain water, which helps to keep the material hydrated during the curing process. This is particularly important in applications such as concrete, where hydration is necessary for the material to gain its full strength.
Other
In addition to its use in cement-based materials, HPMC is also used in other construction applications. It can be used as a thickener and stabilizer in paints and coatings, providing the necessary viscosity and stability to the final product. HPMC can also be used as a binder and thickener in adhesives and sealants, improving the performance and durability of the final product.
Construction grade HPMC is available in various grades, each with unique properties and characteristics. The most common grades of HPMC used in the construction industry are based on the viscosity of the material. Lower viscosity grades are used for applications such as rendering and plastering, where the material needs to flow easily and maintain its shape. Higher viscosity grades are used for applications such as tiling and concrete, where the material needs to be more stable and have a higher bonding strength.
In conclusion, HPMC is a versatile material that is widely used in the construction industry for various applications. Its unique properties such as high water retention, thermal gelation, and film-forming ability make it an essential additive in the construction industry. HPMC improves the performance of construction materials by enhancing properties such as workability, adhesion, water retention, and durability. The availability of different grades of HPMC ensures that the material can be tailored to suit specific applications in the construction industry.
If you want to know more information about HPMC, please contact us. We will provide professional answers.